VoIP Telephony
What is VoIP Telephony?
Since the first accessible VoIP phone appeared nearly 30 years ago, internet telephony has remained one of the most advanced ways to organize communication – especially for businesses. What makes VoIP such an effective tool?
In this article, we will answer this question, explain how VoIP works, highlight its advantages over other communication methods, and show the benefits businesses can gain from using it.
VoIP – what it is and how it works
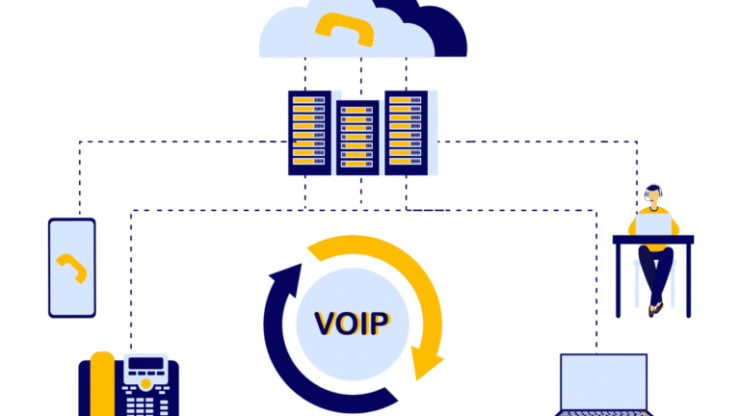
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a communication technology that allows phone calls over a broadband internet connection instead of traditional landlines or radio networks.
VoIP converts voice into digital data packets and transmits them over the Internet, while the provider establishes a connection between callers.
Here’s a brief overview of how VoIP works:
- Voice conversion
When you speak using a VoIP phone or softphone (e.g., KOMPaaS Softphone), sound waves are converted into digital signals via an analog-to-digital converter. - Digital data packets
The digital signals are divided into small packets, similar to how large files are split into parts for internet transfer. Each packet contains metadata, such as the caller and recipient information. - Travel through the Internet
The packets travel through your internet connection to the VoIP provider’s servers. - Routing and codecs
The VoIP provider acts as a switch, determining where to send your call based on the recipient’s number. Specialized software called codecs may compress the data to fit bandwidth limits and ensure high call quality. - Conversion back to voice
On the recipient’s end – whether another VoIP device, landline, or mobile phone – the data packets are reassembled and converted back into an analog signal. - Phone conversation
Finally, the recipient hears your voice through a phone, speaker, or headset – voilà! You are now connected via VoIP.
All that’s needed to start using VoIP is a stable internet connection, an IP phone, or a calling program. If a company still uses analog equipment and PBXs, VoIP adapters or gateways will be required.
Why VoIP is Better than Mobile and Landline Phones
Let’s examine the advantages of internet telephony compared to mobile and landline communication:
Advantages of VoIP:
- Flexibility and portability: Call from anywhere with internet access. Users can make and receive calls via smartphones, computers, or VoIP phones.
- Cost efficiency: VoIP is significantly cheaper than traditional phone services, especially for long-distance and international calls.
- Functionality: VoIP services offer features like call-back for missed calls, automated menus for incoming calls, and more. These functions improve productivity, collaboration, and customer experience.
Main drawback: dependency on internet connectivity.
Advantages of mobile networks:
- Coverage: Wide coverage makes mobile networks reliable almost anywhere.
- Mobility and convenience: Users can stay connected while moving within network coverage.
- Call quality: Generally good quality if within service areas.
Main drawback: expensive international calls.
Advantages of landline phones:
- Reliability: Landlines are stable and less affected by internet outages or mobile network congestion.
- Sound quality: Typically excellent, with minimal interference compared to other methods.
Drawbacks: limited mobility, expensive and complex installation without pre-laid lines, and high tariffs.
In terms of cost and functionality, VoIP clearly outperforms mobile and landline options.
Benefits of VoIP for Business
Modern companies increasingly prefer internet telephony because VoIP positively impacts business processes both in the short and long term.
Key advantages include:
- Cost savings
Call expenses can be reduced by nearly half compared to traditional services, depending on call patterns. - Flexibility
Cloud-based phone systems eliminate bulky equipment, allow distributed teams, and enable call management from anywhere with internet access. - Extended functionality
VoIP offers all standard office PBX features, plus number substitution, IVR with speech generation/recognition, call recording and transcription, video calls, and more. - Scalability
Cloud-based systems can easily scale as the business grows. Adding new numbers does not require new lines, and existing numbers’ capacity can be adjusted as needed. - Advanced analytics
Integration with CRMs, call tracking, and voice analytics allows businesses to monitor call center efficiency and track each customer’s journey.
Conclusion
VoIP is a modern, convenient, and cost-effective business communication tool, outperforming other types of connections in many ways.
Its simple installation and use, affordable calls, quick setup for new offices and remote employees, and ability to leverage the latest telephony features without large capital investment all contribute to its growing popularity among businesses of all sizes and industries.